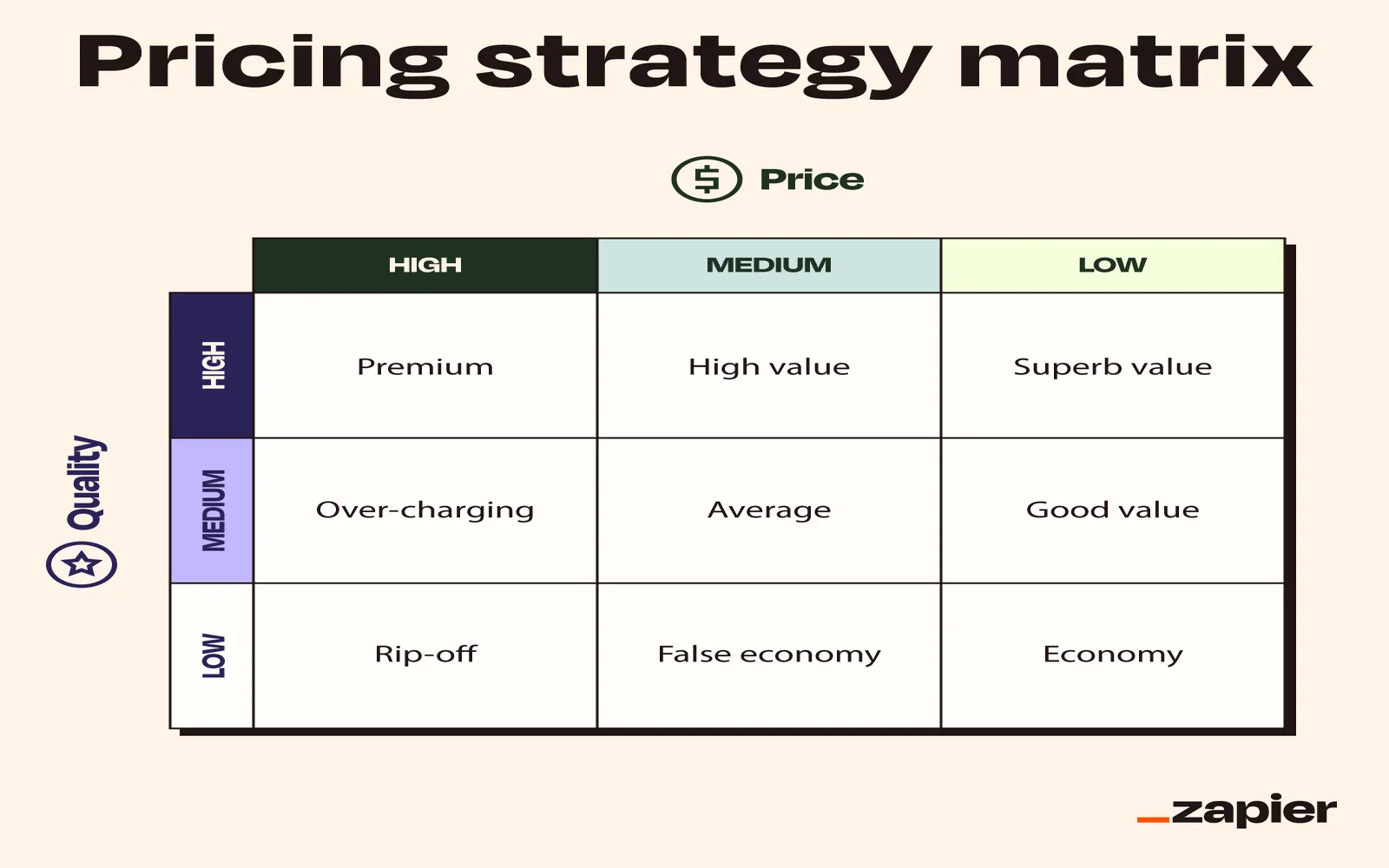
Understanding Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies are integral to any business model. They not only influence customer perception but also play a significant role in a company's profitability. Here, we will explore 16 effective pricing strategies, along with examples and guidance on how to set your own pricing model.
1. Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing involves calculating the total cost of production and adding a markup percentage. For instance, if a product costs $50 to produce and you add a 20% markup, the selling price would be $60.
2. Value-Based Pricing
This strategy focuses on the perceived value of a product rather than the actual cost. For example, luxury brands often price their products based on consumer perception rather than the cost of materials.
3. Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is a strategy used to enter a competitive market by setting a low initial price. For example, a streaming service might offer a discounted subscription rate to attract new users.
4. Price Skimming
Price skimming involves setting a high price initially and then gradually lowering it over time. Technology companies often use this strategy, launching new products at premium prices before reducing them as competition increases.
5. Competitive Pricing
This strategy involves setting prices based on competitors' pricing. Businesses often analyze their competitors’ prices and adjust theirs accordingly. For instance, grocery stores frequently adjust their prices based on local competition.
6. Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing takes advantage of consumer psychology, such as pricing a product at $9.99 instead of $10. This strategy makes the price seem lower and more appealing to customers.
7. Bundle Pricing
Bundle pricing involves offering several products for a lower combined price than if they were purchased separately. For example, fast-food chains often sell combo meals at a discounted rate.
8. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing fluctuates based on market demand, competition, and other factors. Airlines and hotels frequently use this strategy to maximize revenue based on current market conditions.
9. Freemium Pricing
Freemium pricing involves offering a basic product for free while charging for premium features. Software companies often use this model to attract users before converting them to paid plans.
10. Subscription Pricing
With subscription pricing, customers pay a recurring fee at regular intervals. This model is popular with services like Netflix and Spotify, providing a steady revenue stream for businesses.
11. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing offers several pricing levels for different levels of service or features. For example, a cloud storage service might offer a basic plan for free, a standard plan for $10/month, and a premium plan for $20/month.
12. Geographic Pricing
Geographic pricing adjusts the price based on the geographical location of the buyer. This strategy is often used in international markets where purchasing power differs significantly.
13. Promotional Pricing
Promotional pricing temporarily reduces prices to attract customers or clear inventory. Retailers often employ this strategy during holiday sales or special events.
14. Loyalty Pricing
Loyalty pricing rewards returning customers with discounts or exclusive offers. For example, many coffee shops offer loyalty cards that provide a free drink after a set number of purchases.
15. Pay What You Want Pricing
This strategy allows customers to choose how much they want to pay for a product. It can be effective for digital goods, where companies like Humble Bundle allow customers to set their own price.
16. Auction Pricing
Auction pricing involves selling products through bids, where the highest bidder wins. This strategy is prevalent in online marketplaces like eBay, where prices fluctuate based on demand.
How to Set Your Pricing Strategy
Setting your pricing strategy involves several steps:
- Analyze your costs: Calculate all expenses associated with your product, including production, marketing, and distribution.
- Understand your target market: Research your audience to determine what they value and how much they are willing to pay.
- Study your competitors: Analyze competitor pricing and positioning to identify gaps in the market.
- Choose a pricing strategy: Select a strategy that aligns with your business goals and market conditions.
- Test and refine: Implement your pricing strategy and monitor its performance. Be ready to make adjustments based on customer feedback and market changes.
Conclusion
Choosing the right pricing strategy is crucial for business success. By understanding these 16 pricing strategies and applying them appropriately, businesses can maximize their revenue while satisfying customer needs. Whether you choose cost-plus pricing, psychological pricing, or dynamic pricing, ensure your strategy aligns with your overall business objectives.
For those looking to leverage digital marketing strategies, understanding how to optimize your pricing strategy in conjunction with platforms like referrerAdCreative can enhance your overall marketing efforts, allowing you to effectively reach your target audience and drive conversions.